Hacettepe University Faculty Of Medicine
Department Of Child Health And Diseases
Gastroenterology, Hepatology And Nutrition Unit
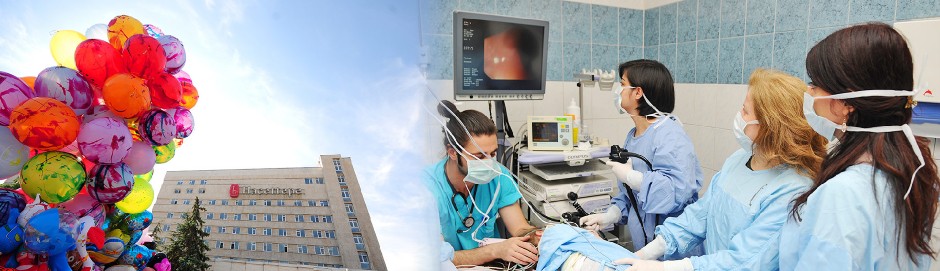
In the unit located in Hacettepe İhsan Doğramacı Children's Hospital, the diagnoses, treatments and follow ups of children with liver and digestive system diseases are carried out and nutritional support is given when needed. Endoscopic procedures - esophagogastroduodenoscopy (visual examination of esophagus-stomach and duodenum with a device with lens at the tail end), colonoscopy (visual examination of the large intestine), rectosigmoidoscopy (visual examination of the last 30 cm of the large intestine)-, 24-hour esophageal pH monitoring (examining whether acid content aspires from stomach to esophagus), capsule or endoscopic biopsy of small intestine , liver biopsy, treatment of patients with bleeding esophageal due to varices with a needle or by ligating, and bone marrow and splenic aspiration for diagnosis of certain genetic diseases withcarried out.
In the unit, there are 1 videoendoscopy system (1 gastroscope and 1 colonoscope), 3 flexible endoscopy devices (2 gastroscopes, 1 colonoscope), 1 rigid (inflexible) rectosigmoidoscopy device, 2 esophageal pH monitoring devices, 1 esophageal multi-channel impedance + pH device (for diagnosis of gastroesophageal reflux) and 1 set of small intestine biopsy capsule (for collecting samples from duodenum without endoscopy) which are used for endoscopic procedures including the ones in neonatal period. There are also electrogastrography device (for measuring electrical activity of the stomach) and motility device (for evaluating contraction and movements of the esophagus, small intestine and large intestine), which are not present in our unit, but can be supplied from adult gastroenterology unit when needed. The needles used for liver biopsy are for single use and different needles are used for each patient. In the unit, there are two beds allocated for performing these procedures. The patients to be proceeded are hospitalized in these beds for the same day or for one night.
It is a procedure performed to determine the severity of damages and/or the causes of liver diseases and a small sample is collected with a special needle. Significant information on disease can be obtained by examining the sample through a microscope.
Firstly, blood tests are performed on the patient who is decided to have biopsy, to determine whether the patient has tendency to bleeding and if biopsy is found to be inconvenient, it is performed after such defects are recovered. Patient is hospitalized on the day of biopsy and monitored for a night following the biopsy. There are no particular procedures to be performed by the patient before biopsy. It is not necessary to fast, unless otherwise stated by your physician. Before biopsy, a medication to calm the patient is given and the site where sample to be collected is numbed by subcutaneous injection.. The pain caused by biopsy is not more than the hip muscle injection. In order to minimize the possibility of bleeding, the patient is laid down on a firm ground, in a position that the biopsy site will be on top, until the following morning. The examination results of the samples collected with biopsy are issued within 7 days, depending on the characteristics of procedures.
In this procedure, which is the way of collecting sample from small intestine for microscopic examination, the patient swallows an olive seed-sized capsule which has a system designed to collect sample. Swallowing the capsule, which is connected to a catheter, does not disturb the patient except a potential mild nausea while swallowing. The patient SHOULD FAST (INCLUDING LIQUIDS) AT LEAST FOR 6 HOURS (4 HOURS FOR INFANTS) in order to prevent vomiting due to nausea, and not to prevent collecting sufficient sample. After the capsule is swallowed, the patient is laid on right laterally for a while (approximately 30 minutes) and the capsule is waited to pass to small intestine with the movements of the stomach. The sample is collected after the capsule is checked with X-ray whether it passed to small intestine. Sufficient sample can be collected from approximately 90% of patients, however it may be necessary to repeat the procedure for the left 10% of patients. Procedure does not cause any pain. The patient is discharged after being followed up for a few hours after the procedure.
After procedure of placing a cylindrical device (7 and 9 mm in diameter) which has a lens at the tail end that enables seeing and has cables inside to reflect the image, through oral passage pharynx, esophagus, stomach and duodenum are visually examined. When needed samples are collected from these sites for microscopic examination.
THE PATIENT SHOULD BE FAST for the procedure to be performed. Since the fasting duration depends on the age of the patient, your physician will inform you while booking the appointment on when the patient should be nourished for the last time. Generally, patients except infants and younger children (first 2-3 years of age) breast-fed, taking baby food or milk, should not eat and even drink water after 24:00 in the midnight.
Before the procedure, the patients are made sleep with medications given intravascularly and they do not remember anything about the operation. In fact, the procedure does not cause any pain, except stimulating the nausea reflex. Occasionally, older patients (over 12 years) do not prefer to be made sleep. Throats of patients in this situation are narcotized with an anesthetic in order to prevent nausea, and their nausee are minimized. These patients are given low doses of sedatives to be calmed, when needed.
The patient is followed up for 2-3 hours and discharged after she/he is observed to wake up and eat following the procedure.
After placing a cylindrical device (7 and 9 mm in diameter) which has a lens at the tail end that enables seeing and has cables inside to reflect the image, through anus, the large intestine is visually examined until the part that it converges with small intestine. When needed, samples are collected from these sites for microscopic examination.
COLON CLEANSING OF PATIENT SHOULD BE MADE for the procedure to be applied. The patient should start a diet that does not cause sedimentation 2 days before the operation and within this period he/she should take medications that help the intestine draining in order to ensure the sufficiency of colon cleansing. When the appointment is booked, you will be informed about which medications and at which doses to use. On the day of the procedure, enema (cleansing of large intestine with a medication applied through anus) is performed to cleanse the fecal residues that will obstruct imaging. THE PATIENT SHOULD NOT BE HUNGRY unless otherwise specified.
Before the procedure, the patients are made sleep with medications and they do not remember anything about the operation. Occasionally, older patients (over 12 years) do not prefer to be made sleep. Low doses of sedative and pain reliever are transfused to them intravascularly, in order to minimize discomfort. After the procedure, the patient is followed up for 2-3 hours and discharged after she/he is observed to wake up and to have no abdominal discomfort.
This procedure can be performed both with the colonoscopy device mentioned above and with a device in the form of a metal tube of 30 cm. As it takes shorter, this device may be preferred in children over 10 years of age, especially when the examination of the last 20-30 cm part of large intestine is required. As it can be performed by cleaning the last part of large intestine with only a medication (enema) applied through anus, without general colon cleansing, it is advantageous that it can be performed on the same day. Biopsy is also performed in this procedure when needed. The patient may be allowed to leave immediately after the procedure.
In some patients, enlarged blood vessels (varix) occur usually on the lower parts of esophagus and they occasionally cause dangerous clinical situations by bleeding. Removal of these varix is aimed with this procedure. The preparations for the procedure are similar with the ones for esophagogastroduodenoscopy. It is a procedure in which an enlarged varices in the esophagus is tied off or ligated by a rubber band delivered via an endoscope.To remove all the varices, the procedure may require to be repeated for a few times.
Instead of rubber band practice, the injection of a solution into the varices with a particular needle that ensures the varices to shrink and be disappeared is used. The procedure may also require to be repeated for a few times, until all varices are totally disappeared.
Percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy/jejunostomy (PEG – PEG/J Gastrostomy is the procedure of placing a tube (a kind of pipe) into stomach through the front abdominal wall, and jejunostomy is placing the tube into small intestine (to jejunum, which is the middle section of small intestines). These tubes may be placed through endoscopy, X-ray or surgery. In our unit, the placement is performed with endoscopy. In this way, before placing the tube, abdominal region in gastrostomy and small intestine in jejunostomy are seen clearly and then the tube is placed.
THE PATIENT SHOULD BE FAST before the procedure. As the procedure is performed by hospitalizing you will be informed on the fasting period by the physician/nurse in the clinic. If you are an all-day visitor, please do not give anything orally to the patient, unless otherwise indicated.
Patients are made fall into sleep with intravascularly administered medications and so they do not remember anything about the operation after the procedure is done. After the operation, your physician will inform you when the patient can start eating. Please do not give anything orally or with tube beyond the knowledge of responsive physician/nurse. If the hospitalization do not due to different reasons, patient will be discharged within 2-3 days after patient/parents are trained about nutrition and ostomy care.
It is the current gold standard for diagnosis of gastroesophageal reflux (Gastric contents are aspirated into esohagus). A catheter (a flexible tube approximately 2 mm in diameter) which has a tip sensitive to pH (acid) alterations is placed into the lower end of esophagus through nose. Outer tip of catheter is connected to a small computer. The pH (acid) alterations in the lower end of esophagus are saved in every 4-8 seconds by transferring the computer system. After recording, the catheter is removed and the data saved in the small computer are transferred to another computer and it is examined whether there is a leakage that would be considered as a disease. As more as the records are saved, more reliable results are obtained, so the procedure is performed on 24 hours a day in the unit. Since the operation cannot be performed without hospitalizing, the patient should stay at least an overnight. AN ALL-DAY VISITOR SHOULD STAY WITH THE PATIENT during hospitalization in order to keep certain records. The hard part of the operation is the first 20-30 seconds when the catheter is passed through the nose.
Patient may feel nausea in the meanwhile. PATIENT SHOULD BE HUNGRY to prevent vomiting. You will be informed by your physician about the required period of fasting in accordance with the age of the child.
It is the current gold standard for diagnosis of gastroesophageal reflux (Gastric contents are aspirated into esohagus ). A catheter (flexible tube approximately 2 mm in diameter) which has a tip including 6 channels to measure the electrical resistance and which is sensitive to pH (acid) alterations is placed into the lower end of esophagusthrough nose. Outer tip of catheter is connected to a small computer. Differently from the esophageal pH monitoring, it can detect the non-acidic refluxes, in addition to the acidic refluxes. Its working principle is based on the relatively higher electrical conductivity of food or liquid compared to air in the event of leakage into esophagus. After recording, the catheter is removed and the data saved in the small computer are transferred to another computer and it is examined whether there is a leakage that would be considered as a disease. As more as the records are saved, more reliable results are obtained, so the procedure is performed on 24 hours a day in the unit. Since the operation cannot be performed without hospitalizing, the patient should stay at least an overnight. AN ALL-DAY VISITOR SHOULD STAY WITH THE PATIENT during hospitalization in order to keep certain records. The hard part of the operation is the first 20-30 seconds when the catheter is passed through the nose.
Patient may feel nausea in the meanwhile. PATIENT SHOULD BE HUNGRY to prevent vomiting. You will be informed by your physician about the required period of fasting in accordance with the age of the child.
It is a simple, reliable and noninvasive test that detects Helicobacter pylori (a bacteria that may cause gastritis and ulcer) in stomach. For the test to give accurate results, it is necessary not to take antibiotics within the last 1 month and stomach medications within the last 1 week prior the test. It is necessary to fast for 4-5 hours before the test. Test takes approximately 30 minutes, at the beginning and at the end of the test samples are collected from breathe that the patient exhales. Thus, the child should be at an age to be able to blow up a balloon. Reports of urea breath test can be received from the secretariat of the outpatient clinic after 16:00 on the following working day.
Collecting sample from bone marrow may be required to diagnosecertain diseases, particularly the genetic diseases (storage diseases). Sample is collected from the femur with a special needle. The procedure is performed as a hip muscle injection and does not disturb the patient more than that. Contrary to common beliefs, it has no detrimental effects on children. Only 1 ml of bone marrow sample which similar to blood is collected. There are no preparations to be made by family, the site that the sample to be collected is numbed during the procedure. A sedative is also given to the patient before procedure when needed. Patient may continue the daily life after the procedure.
If diagnosis cannot be made with bone marrow aspiration, occasionally splenic aspiration is required. It proves particularly useful for the diagnosis of patients with large spleen. The procedure involves receiving a few drops of blood sample from spleen with a needle at the tip of the injector. The pain caused by the procedure is similar with hip muscle injection. The procedure is generally performed on inpatients and they are followed up in terms of bleeding after the procedure.
Examination Appointment
It is recommended for control patients to receive their next appointments, before leaving after the examination when patients leave without receiving appointment or when they desire to change the appointment date, they can book appointments on working days until 17:00 by calling the telephone numbers below. The patients to be examined in the unit for the first time are able to receive appointments after being examined by the door physician. Only the results of patients who were examined previously and whose tests were requested can be obtained and evaluated after 16:30.
Operation Appointments
Operation appointments are not scheduled by telephone. The patient should be examined by the physicians of the unit for the operation to be performed. If an operation is decided according to the examination results, your physician will inform you and arrange an appointment on an appropriate day.
After entering through the door no. 1 of Hacettepe İhsan Doğramacı Children's Hospital, go through the hallway (information desk will remain on your right side) by the information desk (on your left side when you look at the information desk), go up the stairs on the right at the end of the hallway; it is on the first mezzanine.
Telephone:
+90 (312) 305 19 93
+90 (312) 305 19 94




